The World Health Organization (WHO) refers to the number of people who develop vision loss as close to one-third of the global population and lists the main factors that threaten vision health: aging, lifestyle exposures, and infections. They point to the same thing: oxidative stress damage the eyes.
Oxidative Stress and Damage
The body produces oxidative free radicals when it metabolizes oxygen. When negatively disturbed, the body's antioxidant capacity decreases. This is when free radicals seize the opportunity and keep attacking cells - this is oxidative stress and is a significant cause of aging in the body.
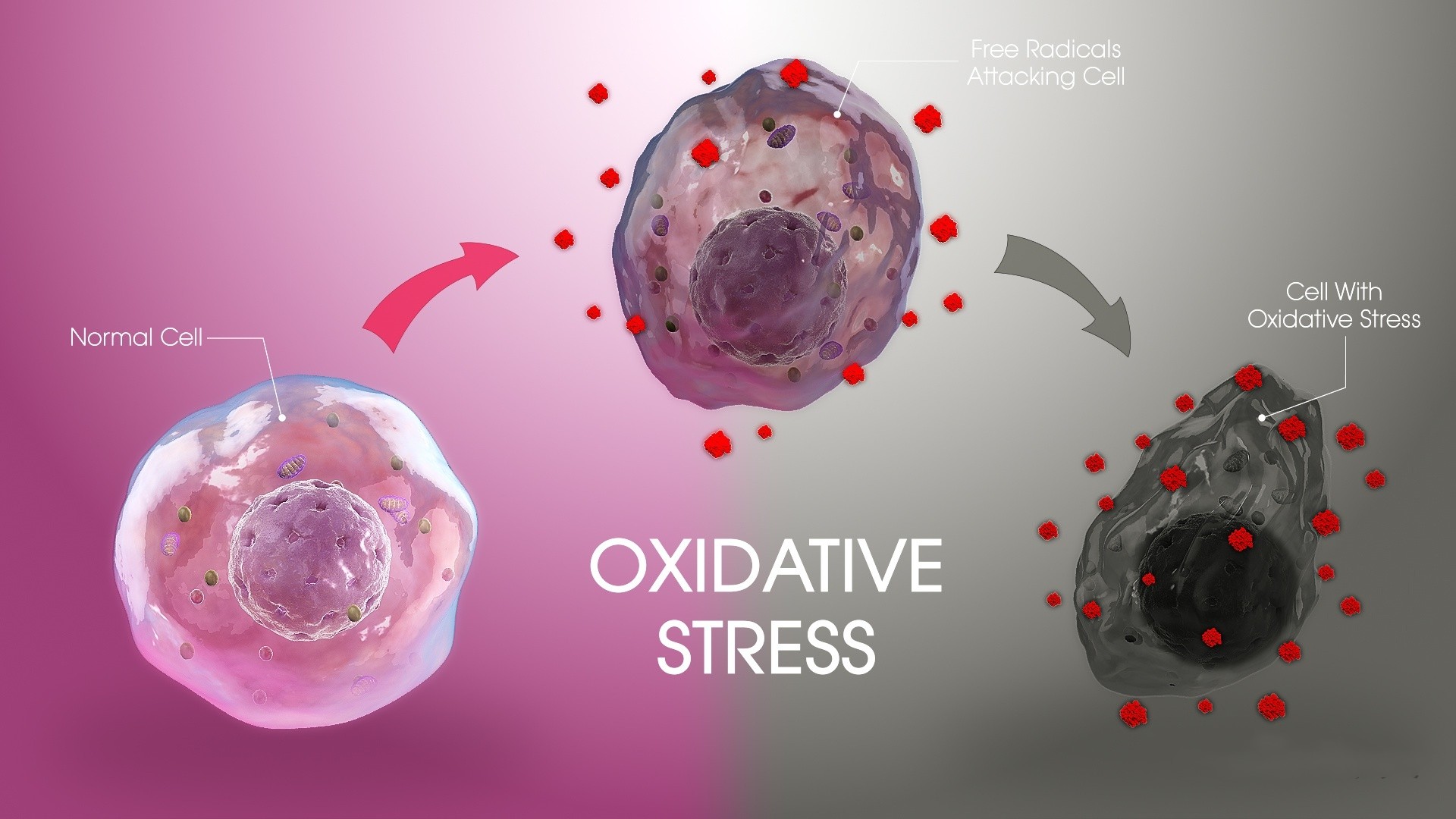
The eyes are a "hardest hit" by oxidative stress.
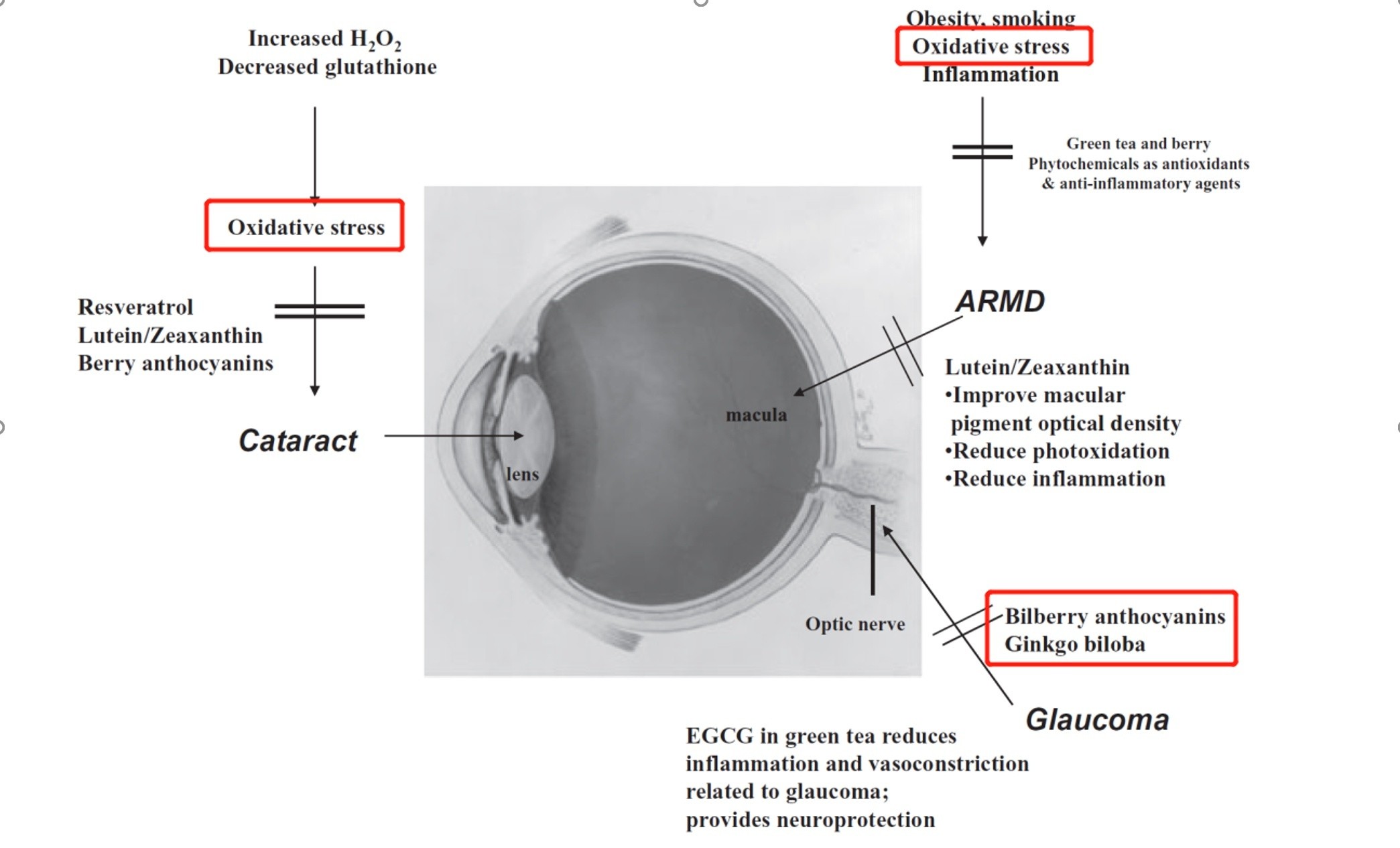
The long and intense working hours of the eyes tend to produce more free radicals; on the other hand, the eyes are directly exposed to the external environment and are also prone to a decrease in antioxidant capacity due to negative interference. In this way, the eyes become a relatively active part of the oxidation reaction. The three eye diseases most likely to cause blindness (cataract, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration) are all related to oxidative stress or reduced antioxidant capacity.
What we can do to prevent?
01 Avoid bright light, blue light, because they damage the eyes in all directions
On the one hand, blue light directly damages photoreceptor cells. It accelerates the oxidation of esters on cell membranes. On the other hand, it inhibits the ability of the body's "antioxidant system" and reduces the efficiency of scavenging free radicals. There are "enzymatic antioxidant systems" and "non-enzymatic antioxidant systems" in the human body; blue light can inhibit the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as peroxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase.
02 Avoid physical, chemical, microbial and other material damage
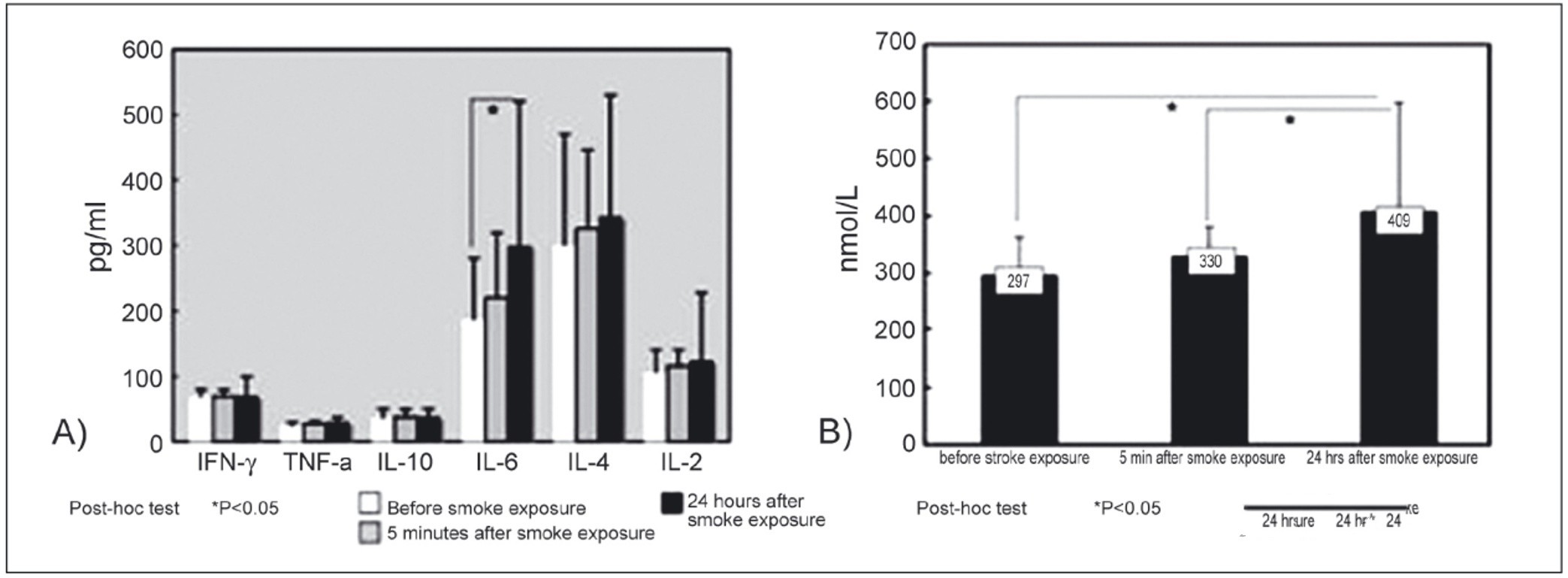
As environmental pollution has increased in the last 20 years, researchers are also paying more attention to the damage to vision caused by pollutants such as smog particles, harmful chemicals, and bacteria. The WHO also makes this point to prevent 'lifestyle exposures.' For example, the World Vision Report explicitly recommends reducing or avoiding 'second-hand smoke' because cigarettes contain many particulates and toxic solid oxides. A 2008 study showed a 37% increase in oxidation products in the eye 24 hours after smoking, proving that oxidative stress is exacerbated.
03 Enhances the ability of the "antioxidant system" to scavenge free radicals
The "antioxidant system" is divided into enzymatic and non-enzymatic. The strength of the "enzyme" system is related to the eyes' overall health. In contrast, the strength of the "non-enzyme" system is directly proportional to the number of antioxidants in the body and can be strengthened through dietary supplementation.
In summary, specific measures that we can use to protect our vision are:
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to bright, blue light and supplementing with nutrients that can filter blue light, such as lutein and carotene.
- Avoiding damage from bacteria, fine particles, and toxic substances, such as reducing smoking or avoiding "second-hand smoke," and paying attention to eye hygiene.
- Use dietary supplements or supplements with fruits and vegetables high in antioxidants such as polyphenols.
Shop our anti-blue-light eyeglasses